Compound for Neutrophil Overactivation, Lower Inflammation
New Compound Shows Great Potential for Patients with Neutrophil-Associated Inflammation
Tags: Hokkaido University, Japan, Healthcare & Lifesciences
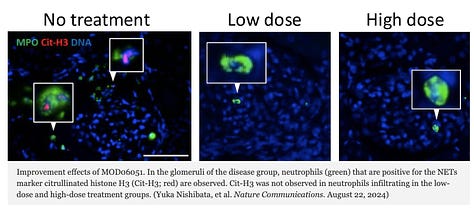
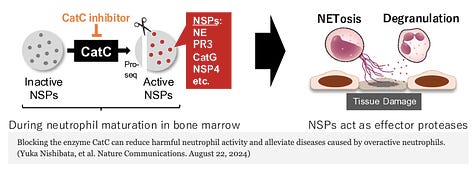
Researchers from Hokkaido University and Alivexis, Inc. have developed a compound, MOD06051, which reduces harmful inflammation in rats by inhibiting Cathepsin C, an enzyme that activates neutrophil serine proteases. This selective inhibition reduces neutrophil elastase activity and limits the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which contribute to diseases like vasculitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Applications of this drug include treating inflammatory diseases caused by overactive neutrophils without broad immunosuppressive effects. The compound shows potential as a safer alternative to current treatments like glucocorticoids. Further research and clinical trials are needed to assess its safety and efficacy in humans.
IP Type or Form Factor: Discovery & Research; Platform
TRL: 4 - minimum viable product built in lab
Industry or Tech Area: Biotechnology; Pharmaceutical Engineering